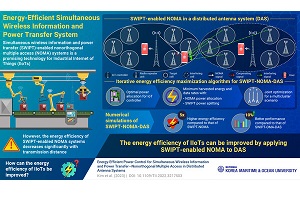
A team of researchers from South Korea, has developed a framework by applying SWIPT (simultaneous wireless information and power transfer) aided NOMA (non-orthogonal multiple access) to a distributed antenna system (DAS). This improves energy and spectral efficiencies of IIoTs (industrial internet of things).
“By applying a DAS with supporting antennas relatively close to edge users alongside a central base station, SWIPT-NOMA’s loss with growing distance can be reduced efficiently. This improves information decoding and energy harvesting performance,” says associate professor Dong-Wook Seo from division of electronics and electrical information engineering at Korea Maritime and Ocean University.
IIoTs refers to a technology that combines wireless sensors, controllers, and mobile communication technologies to make every aspect of industrial production processes intelligent and productive. Since IIoTs can involve several small battery driven devices and sensors, there is a growing need to develop a network for data transmission and power transfer to monitor IIoT environment.
In this regard, wireless power transfer is a promising technology. It utilises radio frequency signals to power small devices that consume minimal power. Recently, SWIPT which utilises a single radio frequency signal to perform energy harvesting and information decoding, has attracted vital interest for IIoTs. Additionally, with smart devices growing in number, SWIPT has been combined with NOMA system, which is a promising candidate for IIoTs due to their ability to extend battery life of sensors and other devices. However, the energy productivity of this system falls with transmission distance from central controller.
The researchers formulated a three step iterative algorithm to maximise energy productivity of SWIPT-NOMA-DAS system. They optimised power allocation for central IoT controller. After that, power allocation for NOMA signaling and power splitting (PS) assignment for SWIPT were optimised jointly, while minimising data rates and harvested energy requirements. Finally, team analysed an outage event in which system cannot provide sufficient energy and data rates, thereby extending joint power allocation and PS assignment optimisation method to multi-cluster scenario.
They validated their algorithm through numerical simulations, finding that proposed SWIPT-NOMA-DAS system is five times more energy productive than SWIPT-NOMA without DAS. Also, it shows a more than 10% improvement in performance over SWIPT-OMA-DAS.
“This technology ensures very efficient energy consumption and offers various advantages such as convenience, low power, and battery life extension. Thus, it can be applied to smartphones, laptops, wearable devices, and electric vehicles. Most importantly, the SWIPT-NOMA-DAS system can optimise resource allocation and efficiently perform wireless charging and information transmission for users in an IoT environment.” adds Seo.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow OR @jcIoTnow
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.iot-now.com/2023/09/20/135653-south-korean-researchers-enhance-iiot-efficiency-with-swipt-noma-in-distributed-antenna-system/
- :has
- :is
- a
- ability
- access
- Additionally
- Adds
- advantages
- After
- algorithm
- allocation
- alongside
- also
- an
- and
- antenna
- applied
- Applying
- article
- AS
- aspect
- Associate
- At
- attracted
- base
- battery
- Battery life
- BE
- been
- below
- by
- CAN
- candidate
- cannot
- central
- charging
- Close
- combined
- combines
- Communication
- consume
- consumption
- controller
- convenience
- data
- Decoding
- develop
- developed
- Devices
- distance
- distributed
- Division
- driven
- due
- Edge
- efficiencies
- efficiency
- efficient
- efficiently
- Electric
- electric vehicles
- Electronics
- energy
- Energy Consumption
- Engineering
- enhance
- ensures
- Environment
- Event
- Every
- extend
- extending
- extension
- Falls
- Finally
- finding
- five
- For
- Framework
- Frequency
- from
- Growing
- Harvesting
- However
- HTTPS
- improvement
- improves
- in
- industrial
- Industrial Production
- information
- Intelligent
- interest
- Internet
- internet of things
- involve
- iot
- IT
- joint
- jpg
- korea
- Korean
- laptops
- Life
- life extension
- loss
- Low
- make
- Maritime
- method
- minimal
- Mobile
- Monitor
- more
- most
- multiple
- Need
- network
- news
- now
- number
- ocean
- of
- Offers
- on
- optimise
- Optimised
- or
- Other
- outage
- over
- perform
- performance
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- power
- processes
- Production
- productive
- productivity
- Professor
- promising
- proposed
- provide
- Radio
- Rates
- recently
- Reduced
- refers
- regard
- relatively
- Reports
- Requirements
- researchers
- resource
- says
- scenario
- sensors
- seo
- several
- Shows
- Signal
- signals
- simultaneous
- since
- single
- small
- smart
- smartphones
- South
- South Korea
- south korean
- Spectral
- station
- Step
- such
- sufficient
- Supporting
- system
- team
- Technologies
- Technology
- than
- that
- The
- their
- There.
- thereby
- they
- things
- this
- three
- Through
- Thus
- times
- to
- transfer
- users
- utilises
- validated
- various
- Vehicles
- very
- vital
- wearable
- wearable devices
- were
- which
- while
- wireless
- with
- without
- zephyrnet