October 9, 2023
At the beginning of 2023, according to IBM Security’s “Threat Intelligence Index” report, healthcare was in the top 10 most-attacked industries on the planet. The “Cost of a Data Breach 2023” report also uncovered that, since 2020, healthcare data breach costs have increased by 53.3%. Even if it adheres to a lot of regulatory practices, for the 13th year in a row, the healthcare industry reported the most expensive data breaches, at an average cost of USD 10.93 million. 58% of incidents were based in Europe, with North American cases comprising the remainder at 42%.
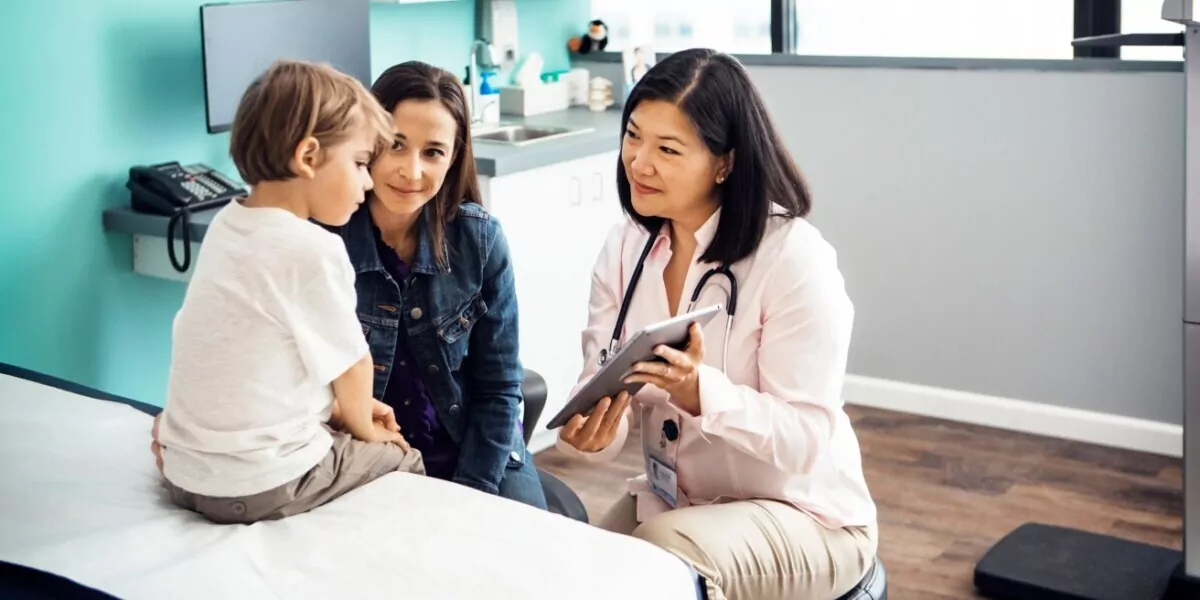
Unified endpoint management (UEM) and medical device risk management concepts go side-by-side to create a robust cybersecurity posture that streamlines device management and ensures the safety and reliability of medical devices used by doctors and nurses at their everyday jobs. UEM is a type of technology that helps manage and secure a variety of endpoints, including mobile devices used in the healthcare ecosystem. These endpoints can also include medical devices or purpose-built devices.
Modern UEM providers develop solutions with a high degree of usability and should provide one platform for overseeing the deployment, security and performance of these devices, managing the product lifecycle and the application lifecycle. Some UEM solutions also include risk assessment capabilities—including AI-powered risk analysis and quick risk evaluation—which would help fit within the industry’s regulatory requirements and perform real-time mitigation of potential cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
Some of the main advantages UEM brings to the companies in the healthcare industry are:
- Visibility: UEM offers real-time visibility into the connected medical devices, enabling healthcare providers to monitor their status, performance, and security. This helps the risk control and limits the probability of the occurrence of data leaks or cyberattacks.
- Smooth deployment: Using UEM solutions, healthcare providers can deploy more easier medical devices such as tablets used by doctors and nurses, configuring them in bulk or separately according to the security policies. One of the main goals is obtaining a frictionless relationship with end users, thus taking into consideration the user needs by default.
- Security Management: UEM provides robust security policies and capabilities, including encrypted containers, single sign-on, identity management, wipe/ remote wipe, and many more. The security capabilities may include dedicated risk management policies, based on real-world industry best practices and regulatory requirements, protecting both the patient data and healthcare providers’ data.
Medical Device Risk Management is prioritizing patient safety through rigorous methodology and risk control.
1. Patient Safety: Ensuring that mobile medical devices are safe and reliable is a must. Risk management processes help identify potential sources of harm and take preventive and protective measures to minimize patient risks.
2. Data Security: In our days, medical devices are interconnected and data security has become extremely important. Medical Device Risk Management strategies contain cybersecurity measures, including specific risk management activities to protect patient data and prevent a potential occurrence of harm such as data leaks or data loss.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Just like healthcare organizations, medical device manufacturers must adhere to strict regulatory guidelines, such as the FDA’s Quality System Regulation (QSR). Proper risk evaluation, risk management processes and methodologies, risk management policies, and risk management activities are paramount for compliance.
4. Life cycle Management: Managing the entire lifecycle of medical devices, including procurement, deployment, and maintenance, is a component of risk management. This is in line with UEM’s core capabilities of managing the product life cycle, for both devices and apps.
There is a clear alignment between UEM and medical device risk management. UEM provides part of the necessary capabilities for implementing solid risk management methodologies and risk management processes within the wider cybersecurity strategy for the healthcare industry:
1. Visibility and Monitoring: UEM solutions offer real-time visibility into medical devices such as special tablets used by nurses and doctors, automatically identifying and performing mitigation of potential sources of harm such as security vulnerabilities and potential cyberattacks.
2. Policy Enforcement: UEM allows healthcare providers to enforce security policies and configurations consistently across all connected devices, with automated risk evaluations. These can be aligned and integrated within the company’s risk management policies. Some UEM solutions have built-in security policies that take into control industry regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
3. Quick Response: In the event of a security breach or device malfunction or if the device was lost or stolen, UEM enables real-time responses, such as isolating affected devices or initiating remote updates and patches. The cybersecurity point of view is that the probability of occurrence of cyber threats or attacks is extremely high and that there are no acceptable levels of exposure. UEM helps contain the business risk associated with cyber threats through risk-based, automatized responses.
4. Data Protection: Through UEM, sensitive data can be encrypted and protected, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations. Modern UEM technology providers cover both USA and European data privacy laws, to help IT teams in the healthcare industry remain productive and efficient. Built-in identity and access management (IAM) features and integration with IAM technologies are a must, to create control measures of what user can access which information.
5. Risk Analysis: Any medical risk management framework specifies methodologies for risk analysis. UEM providers have built-in analytics, some of them powered by AI, which automatically assesses in real-time and with granularity the user risk associated with certain events. These cybersecurity risk analysis features also specifies the measures the IT teams need to take to perform proper risk control, in line with the risk management policies set up by the company and help streamline the decision-making. This can span from stakeholders’ responses to SMS phishing to patches not installed or operating systems that haven’t been updated. Cybersecurity’s point of view has always been that no risk should be passed over, so medical devices and app security should be on the agendas of teams who design controls and create comprehensive risk management processes.
In conclusion, the variety of medical devices in healthcare, such as mobile devices for nurses and doctors, and cyberthreats which are on the rise, ensure that the intersection between UEM technologies and Medical Device Risk Management should be part of any risk management process in a healthcare company. This synergy not only ensures the safety of patient data but also protects sensitive healthcare data, mitigates business risks, and increases the stakeholders’ satisfaction. Cybersecurity risk assessments can evaluate the probability of occurrence of cyberattacks that would contain phishing, ransomware, backdoor attacks, and web shells, and should be part of the development process of a comprehensive risk management process. The AI-powered risk analysis capabilities that some UEM providers offer are part of the cybersecurity assessments and can become an important part of the agenda of any team that designs controls for the healthcare industry. The ultimate goal is to create a holistic, high-level quality of care for patients in a more and more interconnected healthcare ecosystem.
IBM Security MaaS360 is a modern, advanced unified endpoint management platform that helps comply with healthcare regulatory requirements and compliance policies such as HIPAA/HITECH, improve data protection, reduce the strain on the IT workload, and lower the cost of managing mobile devices. MaaS360 has an AI-powered engine that does automatic user risk evaluation so that IT teams can proactively perform mitigation of vulnerabilities and cyber risks.
Learn more about IBM Security MaaS360
More from Cybersecurity

October 3, 2023
Security AI and automation are key in protecting against costly data breaches for retailers and consumer goods businesses
3 min read – The rise of online commerce over the last two decades has completely transformed the retail and consumer goods industries—and with smartphone adoption accelerating globally, the share of shopping done via the internet will only continue to expand. But this growth in digital sales can come with a hefty price tag for retailers and consumer goods businesses: a much greater risk of data breaches. According to a recent study by IBM Security, the 2023 X-Force Threat Intelligence Index established the retail…
<!—->

September 27, 2023
Closing the breach window, from data to action
6 min read – Accelerate threat detection and response (TDR) using AI-powered centralized log management and security observability It is not news to most that cyberattacks have become easier to launch and harder to stop as attackers have gotten smarter and faster. For those defending against cyberthreats, things continue to get more complicated. The list of challenges is long: cloud attack surface sprawl, complex application environments, information overload from disparate tools, noise from false positives and low-risk events, just to name a few. The…
<!—->

September 20, 2023
Spear phishing vs. phishing: what’s the difference?
5 min read – The simple answer: spear phishing is a special type of phishing attack. Phishing is any cyberattack that uses malicious email messages, text messages, or voice calls to trick people into sharing sensitive data (e.g., credit card numbers or social security numbers), downloading malware, visiting malicious websites, sending money to the wrong people, or otherwise themselves, their associates or their employers. Phishing is the most common cybercrime attack vector, or method; 300,479 phishing attacks were reported to the FBI in 2022.…
<!—->

September 13, 2023
Data breach prevention: 5 ways attack surface management helps mitigate the risks of costly data breaches
5 min read – Organizations are wrestling with a pressing concern: the speed at which they respond to and contain data breaches falls short of the escalating security threats they face. An effective attack surface management (ASM) solution can change this. According to the Cost of a Data Breach 2023 Report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach reached a record high of USD 4.45 million this year. What’s more, it took 277 days to identify and contain a data breach. With…
<!—->
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.ibm.com/blog/the-synergy-between-uem-and-medical-device-risk-management/
- :has
- :is
- :not
- $UP
- 1
- 10
- 13
- 20
- 2018
- 2020
- 2022
- 2023
- 27
- 28
- 30
- 300
- 32
- 40
- 400
- 49
- 50
- 53
- 9
- a
- About
- accelerating
- acceptable
- access
- access management
- According
- accountability
- across
- Act
- Action
- activities
- adhere
- Adoption
- advantages
- Advertising
- against
- agenda
- AI
- AI-powered
- aligned
- alignment
- All
- allows
- also
- always
- American
- amp
- an
- analysis
- analytics
- and
- answer
- any
- app
- Application
- approach
- apps
- ARE
- article
- AS
- assesses
- assessment
- assessments
- associated
- At
- attack
- Attacks
- author
- Automated
- Automatic
- automatically
- Automation
- average
- back
- backdoor
- background
- based
- BE
- become
- been
- Beginning
- BEST
- best practices
- Better
- between
- Big
- blockchain
- blockchain network
- Blog
- blogs
- both
- breach
- breaches
- Brings
- Building
- built-in
- business
- businesses
- but
- Buying
- by
- Calls
- CAN
- capabilities
- carbon
- card
- Cards
- care
- cases
- CAT
- centralized
- certain
- challenges
- change
- Charts
- check
- CIS
- class
- clear
- closing
- Cloud
- color
- come
- Commerce
- Common
- Companies
- company
- Company’s
- completely
- complex
- compliance
- complicated
- comply
- component
- comprehensive
- comprising
- computer
- concepts
- Concern
- conclusion
- confident
- connected
- connected devices
- consideration
- consistently
- consumer
- Contactless
- contain
- Container
- Containers
- continue
- control
- controls
- Core
- Cost
- costly
- Costs
- Couple
- cover
- create
- credit
- credit card
- CSS
- custom
- cyber
- Cyberattack
- cyberattacks
- cybercrime
- Cybersecurity
- cyberthreats
- cycle
- data
- data breach
- Data Breaches
- data loss
- data privacy
- data protection
- data security
- Date
- Days
- decades
- Decision Making
- dedicated
- Default
- Defending
- definitions
- Degree
- deploy
- deployment
- description
- Design
- designs
- Detection
- develop
- Development
- device
- Devices
- difference
- digital
- disparate
- Doctors
- does
- done
- e
- easier
- ecosystem
- Effective
- efficient
- Eggs
- employers
- enables
- enabling
- encrypted
- end
- Endpoint
- endpoints
- enforce
- Engine
- ensure
- ensures
- ensuring
- Enter
- Entire
- environments
- established
- Ether (ETH)
- Europe
- European
- European Data
- evaluate
- evaluation
- evaluations
- Even
- Event
- events
- everyday
- Exit
- Expand
- expensive
- Exposure
- extremely
- Face
- Falls
- false
- faster
- fbi
- Features
- female
- few
- fit
- follow
- fonts
- For
- Framework
- fresh
- frictionless
- from
- front
- generator
- get
- Globally
- Go
- goal
- Goals
- goods
- greater
- Grid
- Growth
- guidelines
- harder
- harm
- Have
- Health
- health insurance
- healthcare
- healthcare industry
- height
- help
- helps
- High
- high-level
- holds
- holistic
- HTTPS
- IAM
- IBM
- ICO
- ICON
- identify
- identifying
- Identity
- identity and access management
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- if
- image
- implementing
- important
- improve
- in
- include
- Including
- increased
- Increases
- index
- industries
- industry
- industry’s
- information
- Infrastructure
- initiating
- insurance
- integrated
- integration
- Intelligence
- interconnected
- Internet
- intersection
- into
- IT
- Jackson
- Jobs
- jpg
- just
- Key
- laptop
- large
- Last
- launch
- Laws
- Leaks
- levels
- Life
- lifecycle
- like
- limits
- Line
- List
- live
- locale
- log
- Long
- loss
- lost
- Lot
- low-risk
- lower
- Main
- maintenance
- malware
- manage
- management
- manager
- managing
- Manufacturers
- many
- Marketing
- max-width
- May..
- measures
- medical
- medical device
- medical devices
- messages
- method
- methodologies
- Methodology
- million
- min
- minutes
- Mitigate
- mitigation
- Mobile
- mobile devices
- Modern
- money
- Monitor
- monitoring
- more
- most
- much
- must
- name
- native
- Navigation
- necessary
- Need
- needs
- network
- news
- no
- Noise
- North
- nothing
- numbers
- obtaining
- occurrence
- october
- of
- offer
- Offers
- Office
- on
- ONE
- online
- only
- operating
- operating systems
- optimized
- or
- organizations
- otherwise
- our
- over
- overseeing
- page
- Paramount
- part
- passed
- Patches
- patient
- patient care
- patient data
- patients
- paying
- People
- perform
- performance
- performing
- Peter
- phishing
- phishing attack
- phishing attacks
- photo
- PHP
- planet
- platform
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- plugin
- Point
- Point of View
- policies
- policy
- portability
- position
- Post
- potential
- powered
- practices
- pressing
- prevent
- Prevention
- price
- prioritizing
- privacy
- privacy laws
- probability
- process
- processes
- procurement
- Product
- product lifecycle
- productive
- Programmer
- project
- proper
- protect
- protected
- protecting
- protection
- Protective
- provide
- providers
- provides
- quality
- Quick
- ransomware
- reached
- Reading
- real world
- real-time
- recent
- record
- reduce
- Regulation
- regulations
- regulatory
- relationship
- reliability
- reliable
- remain
- remote
- report
- Reported
- Requirements
- Respond
- response
- responses
- responsive
- retail
- retailers
- rigorous
- Rise
- Risk
- risk assessment
- risk management
- risks
- River
- robots
- robust
- Room
- ROW
- safe
- Safety
- sales
- satisfaction
- Screen
- screens
- scripts
- secure
- security
- security policies
- Security threats
- sending
- sensitive
- seo
- September
- server
- set
- Share
- sharing
- Shopping
- Short
- should
- showing
- Simple
- since
- site
- sits
- small
- smarter
- smartphone
- SMS
- So
- Social
- Software
- solid
- solution
- Solutions
- some
- Sources
- span
- Spear Phishing
- special
- specialists
- specific
- speed
- Sponsored
- start
- Status
- stolen
- Stop
- strategies
- Strategy
- streamline
- strict
- Study
- such
- Surface
- synergy
- system
- Systems
- TAG
- Take
- taking
- team
- teams
- Technical
- Technologies
- Technology
- telecommunications
- text
- that
- The
- their
- Them
- theme
- themselves
- There.
- These
- they
- things
- this
- this year
- those
- threat
- threat detection
- threat intelligence
- threats
- Through
- Thus
- time
- Title
- to
- took
- tools
- top
- Top 10
- transformed
- two
- type
- ultimate
- uncovered
- unified
- updated
- Updates
- URL
- USA
- usability
- USD
- used
- User
- users
- uses
- using
- variety
- via
- View
- visibility
- Voice
- vs
- Vulnerabilities
- W
- was
- ways
- web
- websites
- were
- What
- which
- WHO
- wider
- Wild
- will
- window
- wipe
- with
- within
- WordPress
- Work
- works
- would
- written
- Wrong
- year
- zephyrnet